1981 recession stock market crash causes
A recession implies a fall in real GDP. An official definition of a recession is a period of negative economic growth for two consecutive quarters. Recessions are primarily caused by a fall in aggregate demand. This demand side shock could be due to several factors, such as financial crisis, rise in interest rates or fall in asset prices like houses. Higher oil prices would increase the cost of production and causes the short run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left.
This supply side shock causes lower real GDP and higher inflation.
This is difficult to solve with monetary policy — because we have both inflation and lower output to try and solve. A recession occurs when there is a fall in economic growth for two consecutive quarters. However if growth is very low there will be increased spare capacity and increased unemployment; people will feel there is a recession. This is sometimes known as a growth recession. If there is a fall in AD then according to Keynesian analysis there will be a fall in Real GDP.
A Review Of Past Recessions
The effect on Real GDP depends upon the slope of the AS curve if the economy is close to full capacity lower AD would only cause a small fall in Real GDP. For example, if the MPC increased interest rates sharply this would cause the cost of borrowing to increase and make saving more attractive. This would have the effect of reducing consumer spending. AD could also fall due to deflationary fiscal policy, for example higher taxes and lower government spending would also cause a fall in AD.
If there was a fall in AD the multiplier effect may magnify the initial fall in A. For example if there was a fall in output, workers would be made unemployed.
The IS/LM Model
These workers would then spend less causing a secondary fall in AD. This would make the fall in Real GDP greater. A key feature in determining the rate of economic growth is the level of consumer and business confidence. If confidence was high then higher interest rates may not reduce demand. However if confidence is low and people fear they may be made unemployed, then they will start spending less, causing AD to fall or increase at a slower rate.
An important feature of the UK economy is international trade, therefore the UK would be affected by a global recession.
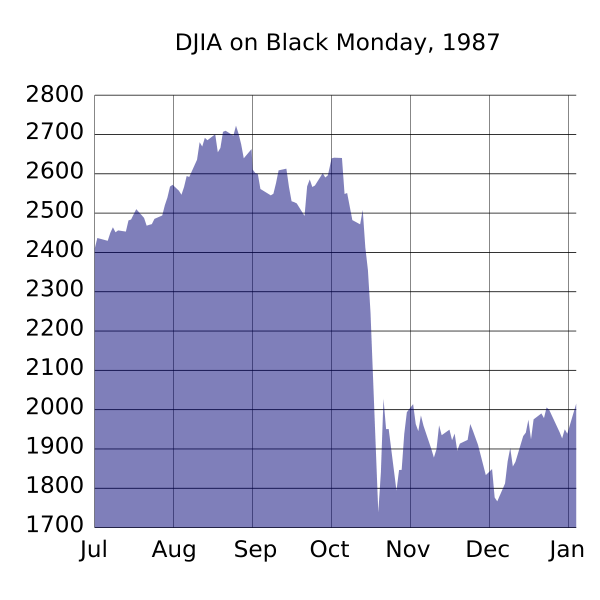
Also a recession in other countries would effect economic confidence if people see the US in a recession they are worried and will spend less. However a global recession may not cause a recession in the UK if domestic demand remains high. Classical Economists believe that any fall in Real GDP will be temporary and will end when labour markets adjust to the new price level.
Classical economists argue that if there is a fall in AD then in the short term there will be a fall in Real GDP.
Causes of an Economic Downturn | Economics Help
However in the great depression of s Keynes was very critical of this classical view he said that the long period of negative growth showed that markets do not automatically clear he argued that this was for various reasons. Facebook RSS Follow economicshelp Basket.
Essay on Causes of Recession A recession occurs when there is a fall in economic growth for two consecutive quarters. Definition of Recessions If there is a fall in AD then according to Keynesian analysis there will be a fall in Real GDP. Wages are sticky downwards, Firms should cut wages to reflect lower prices but in reality workers are very resistant to cuts in nominal wages If wages were cut in response to unemployment workers would have less spending power therefore AD would continue to fall.
In a recession people have low confidence and therefore spend less. What went wrong with US Economy? Get Economics Help See all our Revision Guides. Economic Books - at Amazon. Economic History Causes of Wall Street Crash Causes of Great Depression UK economy in s UK Economy of s UK Economy - s Keynesian Economics Popular posts The problem of printing money The importance of economics Understanding exchange rates 10 reasons for studying economics Impact of immigration on UK economy.
Sections Microeconomics Macroeconomics Labour Markets. Ask an economic question You are welcome to ask any questions on Economics. I try and answer on this blog. About the Author Tejvan studied PPE at LMH, Oxford University and works as an economics teacher and writer. All rights reserved Contact Privacy Policy and Cookies Site by HappyKite.
This site uses cookies More info No problem.